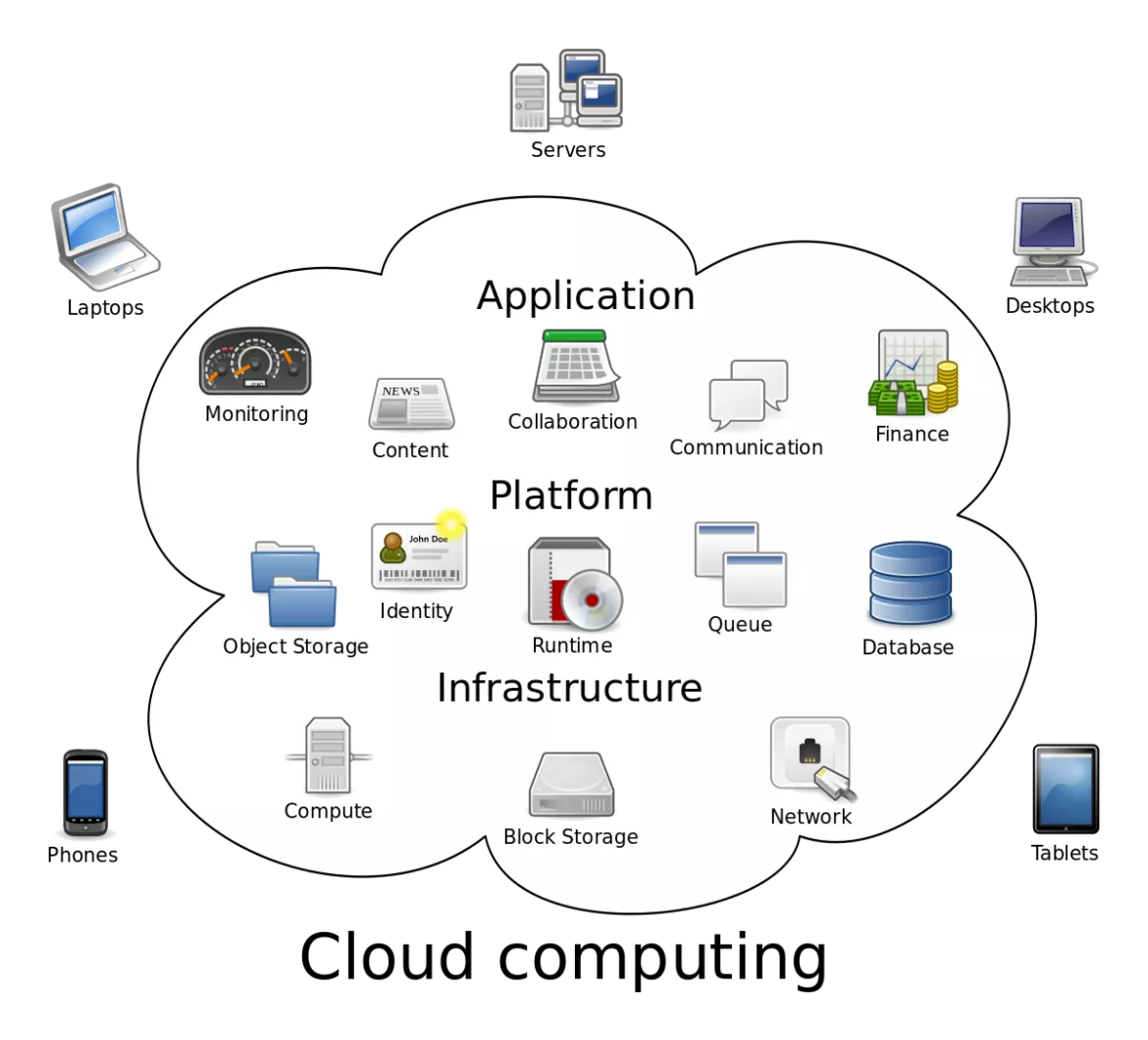
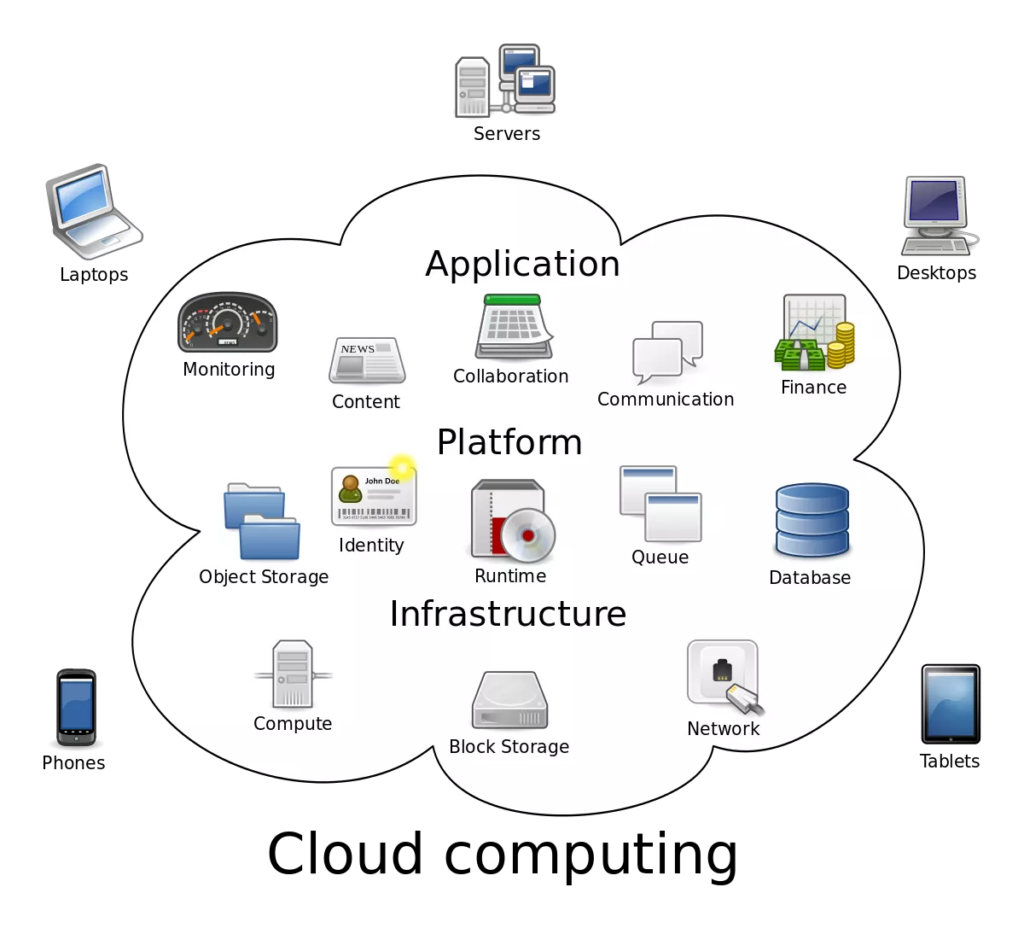
Hardware and software resources are make accessible through the internet as managed outside services in Cloud Computing. These services rely on high-end server computer networks and cutting-edge software programs.
Types of Cloud Computing
Systems for cloud computing are develop by service providers to meet common demands in business or research. Cloud computing services include, for instance:
- Configure and deploy distant external servers as extensions of a company’s local IT network using virtual IT (information technology).
- Use commercial software applications or create and remotely host your own apps for software.
- Network storage: Without needing to be aware of the actual location of the storage, network storage archives data to a provider through the internet.
In general, all cloud computing platforms are build to handle spikes in demand and a high number of consumers.
Software-as-a-Service Models
Software-as-a-service, or SaaS, cloud services offer fully working applications to end users. Even if such programs may not install on those users’ local machines. Most programs that operate in a browser are SaaS apps, including email services like Gmail and Outlook.com. SaaS is therefore most well-known to home users.
Platform-as-a-Service Models
A platform supports a SaaS solution. Platform-as-a-Service vendors often deal with corporate customers. Products offered by PaaS include virtual servers, operating environments, database environments. And any other middleware parts that are use to connect hardware and applications aimed at end users.
Infrastructure-as-a-Service Models
Infrastructure is support by platforms in turn. The level of “bare metal” that infrastructure-as-a-service solutions often reach is that of the actual servers, networking parts. And device storage required to make platforms (and subsequently services) viable. IaaS is well-like by business clients, with each vendor balancing speed, pricing, and privacy in a distinct way.
Services Using Cloud Computing Examples
Various manufacturers provide different kinds of cloud computing services:
- Amazon EC2 — Virtual IT
- Google App Engine — Application hosting
- Google Apps and Microsoft Office Online — SaaS
- Apple iCloud — Network storage
- DigitalOcean — Servers (Iaas/PaaS)
While some service providers offer cloud computing for free, others demand a monthly fee.
How Cloud Computing Works
Instead of sending copies of data files to different client devices, a cloud computing system retains its crucial data on internet servers. Instead of delivering consumers DVD or BluRay physical discs, cloud-based video-sharing services like Netflix, for instance, transmit data over the internet to a player program on the viewing device.
To use cloud services, clients need to connect to the internet. On the Xbox network service, for instance, some video games are only available online (rather than on a physical disc), and some others are similarly unable to play without a connection.
Some business analysts predict that interest in cloud computing will continue to rise in the years to come. One illustration of how all personal computers may change in the future under this trend are devices with little local storage and few local apps except from the web browser, such as the Chromebook (through which online applications and services are reach).
Cloud Computing Pros and Cons
The pros and limitations of cloud computing must carefully consider by developers and users alike, as with any disruptive new technology.
Core cloud technology must install and kept up to date by service providers. This arrangement is preferred by certain corporate clients because it lessens their own maintenance obligations. In contrast, these clients relinquish managerial control over the system and trust on the provider to provide the required standards of performance and reliability.
In the cloud computing paradigm, home users also become very reliant on their internet service provider. As a result, issues like brief outages and slower broadband—which are now minor annoyances—become major issues in a completely cloud-base society. On the other hand, some who support cloud computing say that such an evolution would probably force internet service providers to continually raising the standard of their offering in order to remain competitive.
Systems for cloud computing are often created to keep tight track of all system resources. As a result, service providers can charge clients fees based on how much network, storage, and processing they use. While some customers choose a flat-rate subscription to assure predictable monthly or yearly expenditures, others prefer this metered billing model to save money.
The majority of the time, using a cloud computing environment means sending data over the internet and storing it on a vendor-managed server. This model’s privacy and security issues must be compared to its advantages and available alternatives.
The Consumer’s Bottom Line
The advantages of SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS technologies for the typical non-IT user include reduced costs, quicker deployment times, and greater flexibility. Some individuals would rather have a perpetual license to a piece of software, but others are happy to use subscription-based software that needs an online connection.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What characteristics does a community cloud have?
You can use the following Community Cloud features: Data from other sources and systems may be connected and integrated through business integration. Personalization makes it possible to develop individualized interactions with clients and business partners and enables quicker information discovery. Hope the answer is there.
2. What kind of application uses cloud computing?
A prime illustration of a public cloud is Microsoft Azure. With a public cloud, the cloud provider owns and manages all of the hardware, software, and other supporting infrastructure. Using a web browser, you can get to these services and control your account. Discover more about public clouds. Hope the answer is there.
3. Which programs are employed in cloud computing?
Infrastructure-as-a-Service provided by Amazon Web Services (IaaS) More than 200 cloud computing services are offered by AWS. Compute, storage, analytics, IoT, AI/ML, and database services are among the offered services. AWS now holds a market share of approximately 33% for cloud infrastructure services.