When it comes to car maintenance, one question that often comes up is, “Can I drive with a bad knock sensor?” Technically, yes, you can. In most cases, a faulty knock sensor will trigger the check engine light and store a trouble code in the car’s computer. However, it’s important to understand what a knock sensor does and why it’s crucial for your vehicle’s performance.
Your car is equipped with numerous sensors, each serving a vital function. Among them is the often-overlooked knock sensor, a key component that ensures your engine runs smoothly. Positioned on the cylinder head, intake manifold, or engine block, the knock sensor acts like an ear for your car’s computer, detecting unusual vibrations caused by engine detonation.
In my experience, V engines usually have more than one knock sensor to monitor and maintain optimal engine performance. When a knock sensor fails, you’ll likely notice several symptoms, from decreased fuel efficiency to engine performance issues.
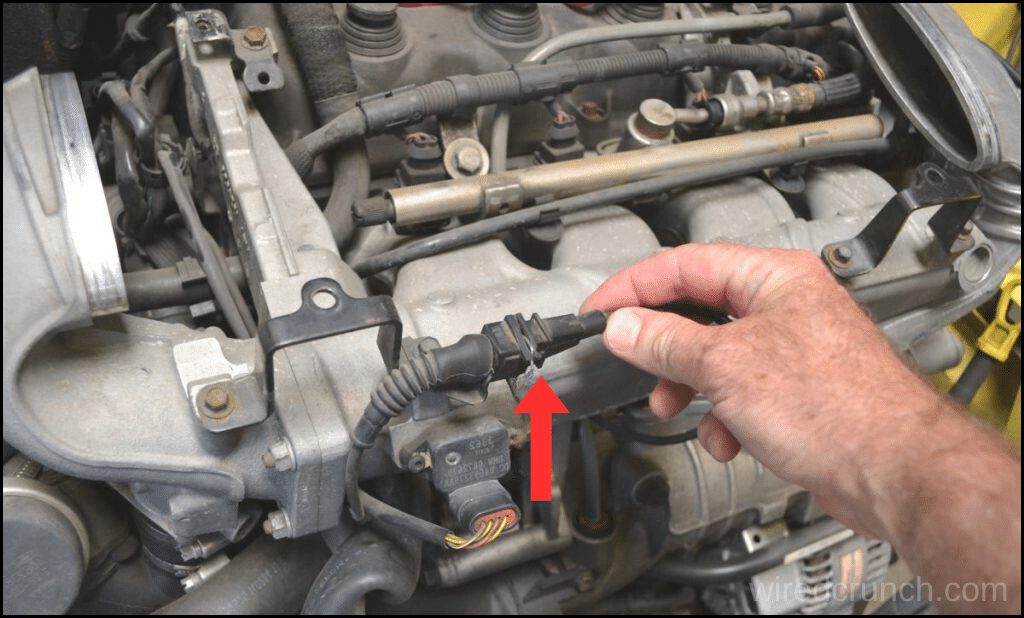
If you’ve ever wondered, “What does a knock sensor do?” or “What does a knock sensor do for a car?” you’re not alone. Let’s dive deeper into the role of the knock sensor and why addressing its issues promptly is crucial for your car’s health.
Table of Contents
What is a Knock Sensor?
Drive with a bad knock sensor can be risky for your car’s engine. The knock sensor uses an internal piezoelectric element to detect abnormal combustion, known as spark knock, inside the engine. Usually located on the left side of the engine block, just below the intake manifold, the knock sensor plays a crucial role in keeping your engine running smoothly.
When it detects vibrations from an engine knock, it sends a signal to the engine control module (ECM). The ECM then adjusts the ignition timing to prevent damage. Found in most gasoline engines, knock sensors help maintain engine performance and longevity by sending an alternating current (AC) signal to the powertrain control module (PCM). If the PCM detects a spark knock, it will retard the ignition timing until the knock stops.
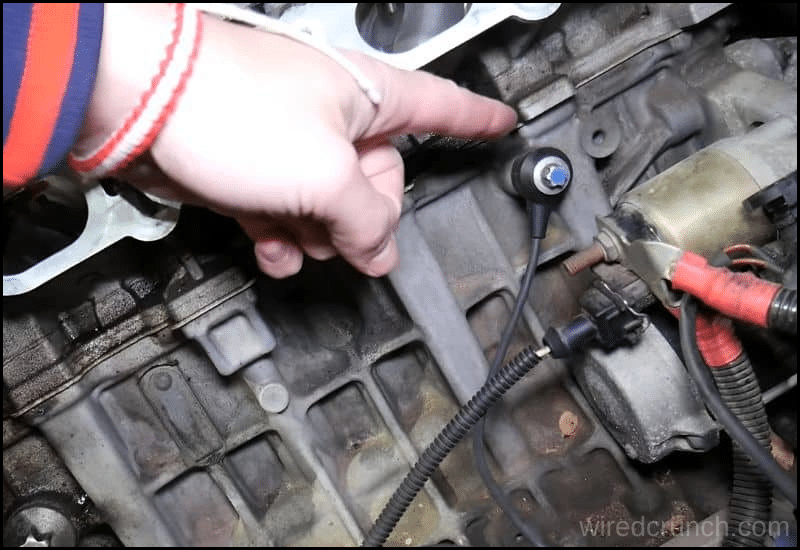
How Do Knock Sensors Work?
A knock sensor, typically mounted on the engine block or cylinder head, detects high-frequency vibrations from engine knocking and converts them into an electrical signal. When the engine runs, the knock sensor monitors for any signs of knocking. If it detects a knock, it sends a signal to the engine control module (ECM), which then adjusts the ignition timing to prevent further knocks.
The ECM uses a microprocessor and algorithms to analyze the sensor’s signal and make necessary adjustments.
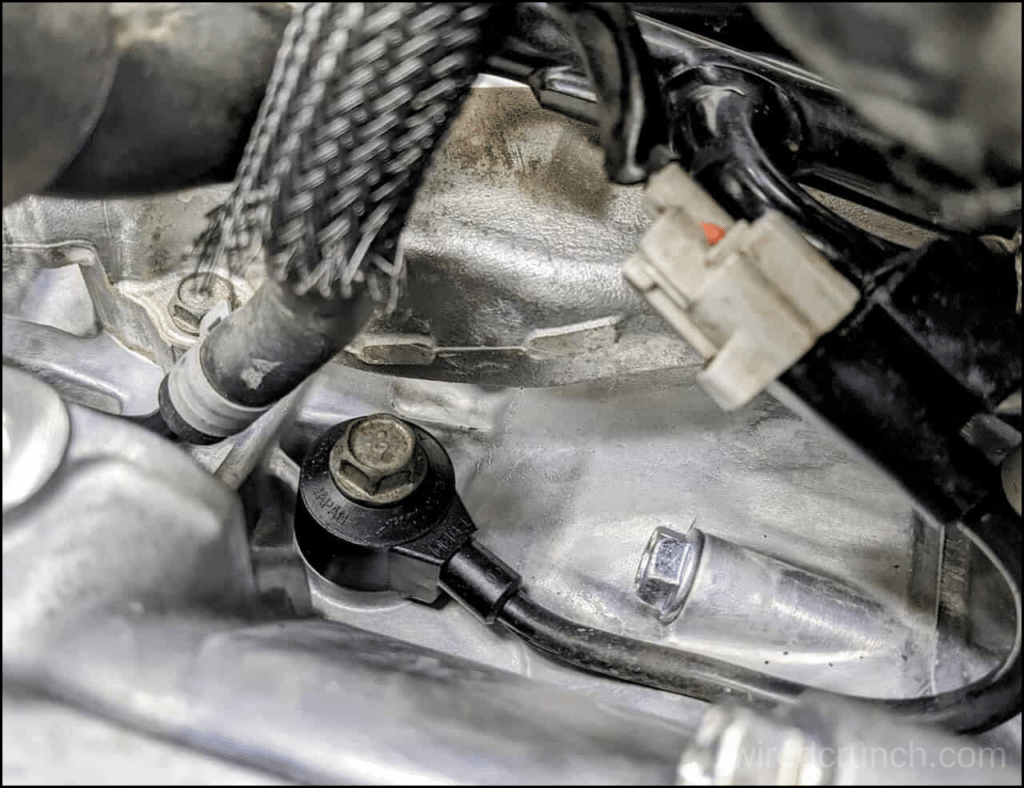
While the knock sensor is crucial, it is only one of many sensors, including the Throttle Position Sensor, MAF, and Oxygen sensor, that the ECM relies on to optimize engine performance.
How long can I drive with a bad knock sensor?
Yes, driving with a bad knock sensor is possible, but it’s not recommended. The knock sensor detects engine knocking and sends signals to the engine control module (ECM), which adjusts the ignition timing to prevent damage. This sensor is highly precise, filtering out spurious noises and only reacting to knocks within a specific frequency range (5 to 7 kHz) and timing window (70° before TDC to 10° after TDC).
Inside the sensor, a piezo ceramic disc generates voltage spikes when under pressure from engine knocks. The ECM uses these signals to make real-time adjustments, retarding the timing only for the affected cylinders. Without a functioning knock sensor, the ECM can’t properly manage these adjustments, which can lead to engine damage over time.

Common Symptoms Of Bad Knock Sensor
When the knock sensor fails, you’ll usually notice one or more symptoms. The most common problems with the knock sensor include:
Check Engine Light is on
Among the signs of bad knock sensor, the most common is the check engine light turning on. When the PCM detects an issue with the knock sensor or its circuit, it activates the check engine light and stores a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) in its memory.
A pinging noise from the engine
If the knock sensor fails, the PCM may not detect or fix the spark knock. As a result, you might hear a metallic pinging noise from the engine, especially when the engine is under heavy load.
Poor engine performance
A faulty knock sensor can cause the PCM to misadjust the ignition timing, leading to poor engine performance. While it’s rare for a bad knock sensor to prevent your car from starting, it can make starting more difficult.

How to Test a Knock Sensor
It’s wise to test a suspected knock sensor before buying a new one. Make sure to have the vehicle’s repair information ready. Manuals like Chilton are helpful, but a subscription to a repair database like ALLDATA or Mitchell 1 DIY is even better. For more details on accessing quality repair information, check our article on repair manuals.
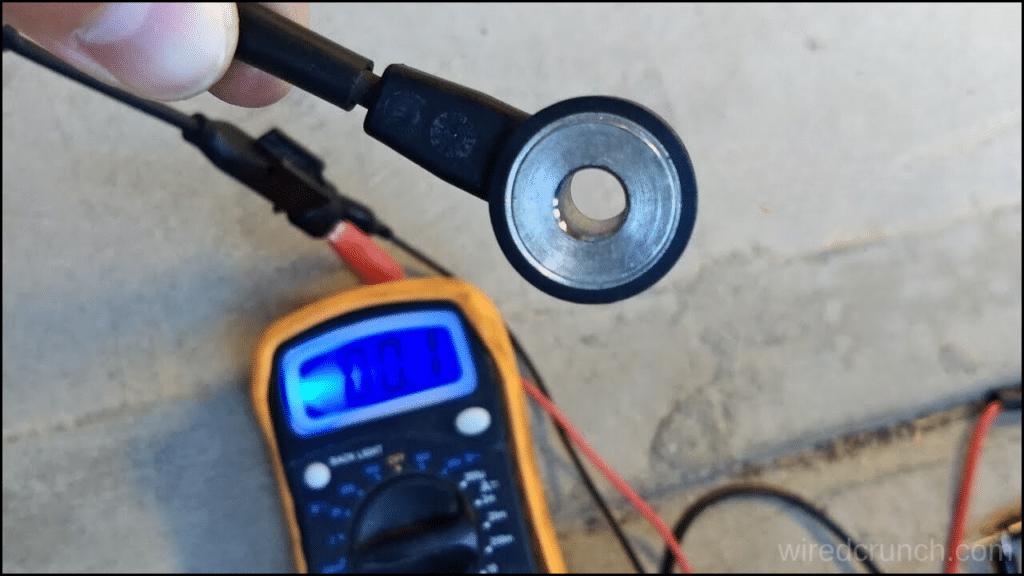

Step 1: Check for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
If you’re dealing with a bad knock sensor, start by checking for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). Cars made after 1996 with OBD II will usually set a code for knock sensor issues, and some older cars with OBD I can do the same. Use a scan tool or an OBD II code reader for your smartphone to check for codes. Remember, DTCs don’t give the exact problem but help narrow down the issue for further inspection.
Step 2: Perform a Visual Inspection
The next step is to perform a visual inspection. Look for issues like damaged wires and poor connections. Ensure the knock sensor’s electrical connector is clean and securely attached. Fix any problems you find during the inspection, clear the DTCs, and check if the issue reappears.
Step 3: Test the Knock Sensor Directly
Testing a knock sensor can be tricky, especially if you suspect you have a bad knock sensor. The two main types of knock sensors are wideband piezoelectric and resonance piezoelectric. Wideband sensors pick up vibrations across a range of frequencies, while resonance sensors respond only to vibrations in the same frequency range as spark knock, typically between 5,000 and 9,000 Hz. These resonance sensors are sometimes called “tuned” knock sensors because they’re specifically tuned to detect spark knock frequencies.
In the past, with more common wideband sensors, a simple test involved tapping the engine near the sensor and observing its response. However, this method doesn’t work with newer resonance-style sensors. Most professionals now test these sensors by forcing the engine to ping (exhibit spark knock) while monitoring the sensor’s output signal to ensure it responds correctly.
Pro Tip: Some Toyota engines might not start if the knock sensor fails, but you’ll usually see a trouble code indicating this issue. It varies depending on the platform and manufacturer.
Replacing a bad knock sensor
Replacing a knock sensor can be done in just a few easy steps. Here’s how it’s done in most vehicles:

Remove the undertray
The undertray protects vital engine parts from debris, dirt, and moisture. Removing it allows access to the engine components underneath. The number and type of attachments holding the undertray in place can vary depending on the car model.
Remove components to access the sensor
In some vehicles, the knock sensor is hidden behind other components you’ll need to remove first. Ensure other wires and connectors are out of the way to avoid accidentally disconnecting them while you clear the path to the sensor.
Remove the knock sensor
Unscrew the bolt securing the knock sensor in its housing. Once the sensor is free, follow the wiring to the electrical connection securing it to the vehicle. Disconnect the connector, and the sensor will be completely removed from the engine.
Replace the knock sensor
Connect the new knock sensor to the electrical connector and secure it in place. Insert the bolt through the sensor and tighten it.
If your engine has multiple cylinders and you have a bad knock sensor, additional knock sensors may be needed. It’s recommended that all knock sensors be replaced at once. Follow the same removal and replacement steps for each sensor to ensure they are all installed correctly.
Conclusion
How long can I drive with a bad knock sensor? You can continue driving with a faulty knock sensor, but if you observe unusual engine noises, performance issues, or irregular running, it’s crucial to scan for diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) or have the vehicle inspected. Look specifically for knock sensor DTCs to determine if the sensor is the source of the problem.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What happens if a knock sensor goes bad?
This is because a faulty knock sensor can cause the ECU to adjust the ignition timing incorrectly, resulting in poor combustion and wasted fuel. Engine misfires can lead to various issues, including higher emissions, lower fuel efficiency, and harm to the catalytic converter.
What happens if you don’t fix your knock sensor?
If a faulty knock sensor isn’t replaced it can lead to other issues like poor acceleration, degraded emissions, or total power loss.
Is the knock sensor code serious?
Can you drive with a P0325 code? Technically, you can, if you have to—but you shouldn’t. Driving with the P0325 error code set for a prolonged period can potentially cause major engine damage. Be sure to address the issue right away.
Can you replace a knock sensor yourself?
Is it possible for me to replace the knock sensor on my own? Most people can replace a knock sensor, and very few basic tools are needed — but diagnostics can be tricky. The sensor must be diagnosed correctly. If diagnosing the switch becomes challenging or unmanageable, it’s best to reach out to a professional for assistance.
How does a bad knock sensor affect a car?
A knock sensor in a car is designed to detect abnormal combustion in the engine, often referred to as “engine knock” or “pinging.” When the knock sensor detects these abnormal vibrations or sounds, it sends a signal to the engine control unit (ECU) to adjust the ignition timing and prevent potential engine damage.
READ MORE:
How Much Does a Transmission Fluid Pressure Sensor Replacement Cost
How to Fix Pre collision Assist not Available Sensor Blocked Error
I have a professional background with a Diploma in Information Communication Technology, which brings a blend of technical expertise and creative flair to my writing. Currently, I serve as a writer for Creativeoutrank LLC and contribute to their various websites.
I’m writing is a ref... Read more


